Note: If an image ever fails to appear - refresh your page, it really is there
Historical and Current Flags of the European Union
(Including Important Institutional and Honor Flags)
The European Union (EU) is an economic and political union of 27 member states which are located primarily in Europe. Important institutions of the EU include the European Commission, the Council of the European Union, the European Council, the Court of Justice of the European Union, and the European Central Bank. The European Parliament is elected every five years by EU citizens. The 27 members of European Union are: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, The Czech Republic, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, The Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
It's currency, the euro is used in 14 countries of the European Union: Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Greece, Slovenia, and Slovakia. In spite of not being members of European Union, Andorra, the Holy See, Monaco, and San Marino also use the euro as their currency.

Council of Europe
(Early Reported Variant)

EEC/EC/EU Flag

Unofficial EU Flag 1985
(variant rarely seen or used)
|
Council of Europe 1955
European Economic Community 1983
European Union 1993
The European Union (EU) traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the European Economic Community (EEC), which was formed by six countries of Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg and the Netherlands in the 1950s. The Council of Europe should not be confused with the European Union, although both organizations use the same flag. The CoE and EU are quite distinct. The CoE is a 47-member international organization dealing with human rights and rule of law, while the EU is a quasi-federal union of 27 states focused on economic integration and political cooperation. The 27 European Union states, however, are all members of the Council of Europe.
The European Economic Community (EEC), also known as the Common Market, was founded in 1957. In 1979, the first European elections were held using universal suffrage. In 1983, the European Parliament adopted the EU flag for the European Community, and in 1993, the name European Union was adopted. Since the EEC was reformed into the European Union (EU) in 1993, the EU has grown in size and in power by the accession of new member states.
The Flag of Europe is the flag and emblem of the European Union (EU) and Council of Europe (CoE). It consists of a circle of 12 golden (yellow) stars on a blue background. It was created in 1955 by the CoE and adopted by the EU, then the European Community, in the 1980s. It was the intention of the CoE that the flag should come to represent Europe as a whole, and since its adoption the membership of the CoE covers nearly the entire continent.
An unofficial European Community flag was displayed on the occasion of a visit to the European Commission in Brussels (Belgium) by His Holiness Pope John Paul II, on May 20, 1985. This EEC flag was blue with a yellow symbol consisting of a single round "E." |
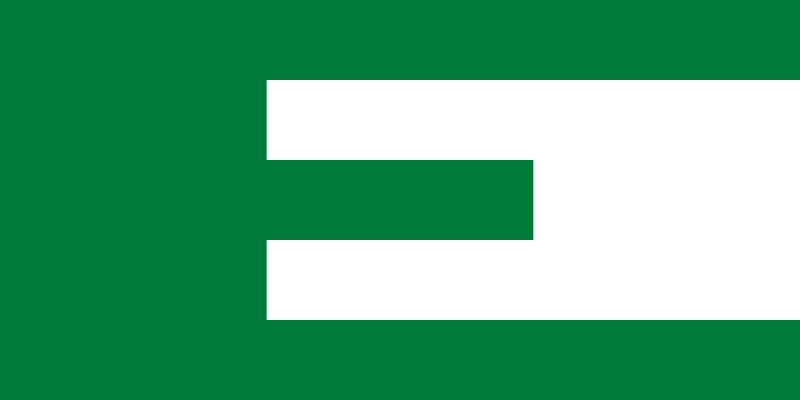
Green "E" Flag
|
Flag of the European Movement 1949
The old flag of the European movement (EM), used up to the adoption of the European flag with the ring of twelve stars by the Movement. This flag is still used by the Union of European Federalists (UEF) and is now often called "Federalist Flag."
The flag first appeared at the Congress of Europe in 1948 which was organized by the International Committee of the Movements for European Unity (MEU), however the color of the E was red. The congress demonstrated the first divisions between Unionists and Federalists (those wanting a loose union and those wanting a United States of Europe). The Congress led to the creation of the European Movement and, at its first meeting in Strasbourg in September of the same year, adopted the "E" flag, but changed the color red to green. It is speculated that the man most likely to have proposed it was Duncan Sandys, who was responsible for developing the British European Movement. The flag was first flown in London in 1949 at the European Economic Congress.
|

ECSC Flag

ECSC Flag
(after 1986)
|
European Coal and Steel Community 1951-2002
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was a six-nation international organization (Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, and The Netherlands) atempting to unify Western Europe during the Cold War and create the foundation for the modern-day developments of the European Union. The ECSC was the first organization to be based on the principles of supranationalism.
The ECSC was first proposed by French foreign minister Robert Schuman in 1950 as a way to prevent further war between France and Germany. He declared his aim was to "make war not only unthinkable but materially impossible." The means to do so, Europe's first supranational community, was formally established by the Treaty of Paris in 1951. Between these states the ECSC would create a common market for coal and steel.
The ECSC, which later merged with the European Economic Community (EEC) in 1967, at first used a flag with six golden stars, but after 1986 used a twelve star version indicating the growth of its membership.
In 2002, the Treaty of Paris expired, and with no desire to renew the treaty, all the ECSC activities and resources have been absorbed by the European Community.
|

EPPE Flag
|
Flag of the European Parliament, 1973-1986
The European Parliament (EP) is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union (EU). The Parliament is composed of 736 MEPs (Members of the European Parliament), which makes it the second largest democratic electorate in the world, representing over 375 million eligible voters.
This flag with the yellow letters "EP" (European Parliament) and "PE" (Parlement Europeéen) surrounded by a yellow wreath, all on a blue background, was used between 1973 and 1986 by the European Parliament, although never officially adopted. After 1986, the Parliament used the standard EU Flag.
|

WEU Flag
1867
|
Flag of the Western European Union 1954-2010
The Western European Union (WEU - Union de l'Europe Occidentale), established in 1948, the Treaty of Brussels established a military assistance pact between the United Kingdom, France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg. In 1952, the USA proposed the idea of an European Defense Community integrated to NATO. The project was rejected by the French Parliament in 1954, and the Western European Union was created in 1954 by a new European pact signed in Brussels, allowing the rearming of Federal Republic of Germany and its integration in WEU and NATO.
The Western European Union should not be confused with the European Union, although its member nations are all part of the EU. The present membership of the Western European Union includes: Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain and United Kingdom. The WEU was officially disbanded in 2010.
|

WEU Flag
|
Flag of the Assembly of the Western European Union 1954-2010
The Assembly of the Western European Union is an assembly for delegations from the national parliaments of the member countries of the Western European Union (WEU), a security and defence organization.
The flag of the Assembly of the WEU is blue with a white dove rising from yellow lines of stylized assembly seats surrounded with 12 yellow five-pointed stars in perspective and below in an arch white inscription "UEO-WEU."
|

Flag of Honour
|
Flag of Honour of the Council of Europe since 1961
A special honor by the Council of Europe is awarded each year by the Committee on the Environment, Agriculture and Local and Regional Affairs of the Parliamentary Assembly to one or more municipalities which have in the Committee's opinion made outstanding efforts to propagate the idea of European unity. More than 1,000 of these Flags of Honour have been awarded by the Council of Europe since 1961.
The Flag of Honour of the Council of Europe is similar to the flag of the Council of Europe, but with a light shade of blue and a golden fringe. Two blue sashes are attached to the flag, bearing the yellow writing "Conseil de L'Europe" in French and "Council of Europe" in English.
|

Heritage Flag
|
Flag of the European Heritage Days 1996
In 1996, the European Heritage Days, sponsored by the Council of Europe, were celebrated in 46 European countries. Several institutional buildings, museums and private places of cultural interest were opened to the public just for those days. In France, the celebration is also sponsored by the Ministry of Culture, which releases every year pamphlets listings all the open places.
The flag of the European Heritage Days is the European Union flag charged with a white skyline made of houses, a church steeple, a defence tower and a dome, thus reflecting the diversity of the European cultural heritage. This flag is hoisted daily in Lisbon (Portugal) in the local office of the European Council's European Heritage Network.
|

Belgium EU Flag

Italy EU Flag

The Netherlands EU Flag
|
Unofficial EU Civil Ensigns
It has became more and more common to see ships hoisting what could be called a European Civil Ensigns, made of the European Union flag with the national flag of one of the member countries in canton. The origin of these flag is unknown, and the country where they first appeared is also not known, but the use of these flags has been increasing in popularity over recent years, and more are expected to appear in time.
|
|
|
Germany EU Flag |
|
Slovenia EU Flag |
|
|
|
France EU Flag |
|
Greece EU Flag |
Because these flags are at present unofficial, they should not be used to replace official civil ensigns. These un-official ensigns have been reported in use in Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Slovenia, and the Netherlands.
|

EU Twinning Flag
|
European Union Municipality Twinning Flag
This flag is an example of a EU Municipality Twinning Flag. In this case, the Town of Andernos-les-Bains, located on the Arcachon Bay in France, is twinned with the towns of Nussloch (Germany, 1977), Segorbe (Spain, 1993), and Large (Scotland, 2008). This twinning partnership is celebrated by a variant of the European Union flag, hoisted together with the French flag and the municipal flags in several places, including the promenade and traffic circles of the town.
This flag has four small flags in the corners, French in upper left corner, German in upper right corner, Scottish in lower left corner, and Spanish, without the arms, in the lower right corner.
|
Flags of Other Related European Agencies and Offices
Agencies of the European Union are organizations which were established to accomplish specific tasks. Some answer the need to develop scientific or technical know-how in certain fields, others bring together different interest groups to facilitate dialogue at both European and international levels.

CEPOL Flag
|
European Police College
Its objective is to reinforce the cooperation between the national police schools of the European Union in order to stimulate a common approach of the most important problems in fields such as the fight against crime, peacekeeping, civilian crisis management, etc. CEPOL's activities are primarily aimed at senior officers of police forces who will benefit from training sessions based on common standards. But, in practice, CEPOL also organises specialised training courses for policemen at intermediary level and policemen in the field, for the trainers themselves and for those policemen who play an important part in the issues which CEPOL organises training sessions about.
Its flag is white with its oval emblem and its name under it with blue lettering.
|

CERN Flag
(Birth place of the WWW)
|
European Organization for Nuclear Research
The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN - Conseil Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire is an international organization whose purpose is to operate the world's largest particle physics laboratory, which is situated in the Northwest suburbs of Geneva on the Franco-Swiss border. Established in 1954, the organization has twenty European member states. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
It is interesting to note that it was in 1989 at CERN that a British computer scientist, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, first proposed a project that would eventually become the World Wide Web. A year later, Belgian computer scientist Robert Cailliau and Berners-Lee further proposed to use hypertext machine Language (HTML) as the common coding for the internet.
|

CNCE Pennant
|
Nautical Circle of the European Communities Pennant
The Nautical Circle of the European Communities (CNCE - Cercle Nautique des Communautés Européennes), is a sailing and boating club registered at Brussels especially for European Union staff members, their families and friends which offers a wide range of nautical activities and services. Membership is open to any official or agent working at the European Institutions as well as to their family members or friends.
The burgee of the CNCE is blue with a thin yellow border, it has the European ring of 12 yellow stars in canton, the silhouette of a white sailboat and the white letters "CNCE" at the point of the flag.
|

EASA Flag
|
European Aviation Safety Agency
The European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) main mission is to promote the highest common standards of safety and environmental protection in civil aviation. The Agency develops common safety and environmental rules for its European members and monitors the implementation of standards through inspections in the Member States and provides the necessary technical expertise, training and research. The Agency works hand in hand with the national authorities which continue to carry out many operational tasks, such as certification of individual aircraft or licensing of pilots.
It was created in 2002 and is headquartered in Cologne, Germany. Its flag is blue with its logo on it. The logo consists of three white stars, the upper one is overlapped by a yellow flying bird.
|

ECDC Flag
|
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) is an independent agency of the European Union (EU) aimed at strengthening Europe's defences against infectious diseases. While the idea of creating a European CDC had been discussed previously by public health experts, the outbreak of SARS in 2003 and its rapid spread across countries confirmed the urgency of the creation of an EU-wide institution for public health. ECDC also publishes scientific and technical reports on various issues related to communicable diseases prevention and control, including comprehensive reports from key technical and scientific meetings. It was established in 2005 and seated in Stockholm, Sweden.
The flag of the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control is white with its logo in the middle of the flag, with two panel, green in upper, and blue in lower part. Despite its vertical rectangular shape (taller than it is wide), the flag is normally flown horizontally so the logo appears upright.
|
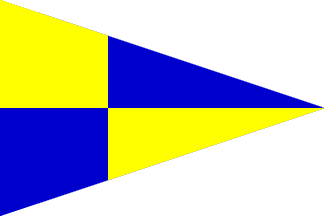
ECF Pennant
|
European Commission of Fisheries
This flag is hoisted by the European Union Fishery Inspection (ECF) vessels in the waters of European Union. The European Commission plays a leading role in developing EU fisheries law. These include the areas of maritime transport, fishing, aquaculture, oil and gas extraction, use of wind and tidal power, shipbuilding, tourism and marine research. The EU countries have decided to manage their fisheries in collaboration, through the common fisheries policy (CFP). This policy brings together a range of measures designed to achieve a thriving and sustainable European fishing industry.
The ECF is under the leadership of the European Commissioner for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries. The flag hoisted by the fishery inspection vessels in the waters of European Union is a triangular flag quartered blue and yellow. The flag was adopted in 1987.
|

ECHA Flag
|
European Chemicals Agency
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) system. It is sited in Helsinki, Finland.
Its flag is white with a blue rounded panel where logo is placed. Under the logo, abbreviation of the Agency can be seen with black letters. Logo consists of EU stars and a white emblem formed from letters of ECHA.
|

EDA Flag
|
European Defence Agency
The European Defence Agency (EDA) is an agency of the European Union based in Brussels. It is a Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) body set up in 2004. EDA was established to support the Member States and the Council in their effort to improve European defence capabilities in the field of crisis management and to sustain the European Security and Defence Policy as it stands now and develops in the future. All EU member states, except Denmark, which has opted-out of the CFSP, take part in the agency. Norway, which is not an EU member, has been granted rights to participate in the EDA programs without voting rights.
The EDA flag is the EU flag with yellow EDA letters in the middle of the circle of stars.
|

EEA Flag
|
European Environment Agency
The European Environment Agency (EEA) is an agency of the European Union. Their task is to provide sound, independent information on the environment. It is a major information source for those involved in developing, adopting, implementing and evaluating environmental policy, and also the general public. Currently, the EEA has 32 member countries. They are 27 EU member states and 4 EFTA members: Iceland, Norway, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, and 1 EU candidate country: Turkey. It became operational in 1994, and is headquartered in Copenhagen, Denmark.
Its flag is white with its emblem on it. The emblem consists of a green flower and a blue cogwheel.
|

EMCDDA Flag
|
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction
The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) was established in 1993. Inaugurated in Lisbon in 1995, it is one of the EU's decentralized agencies.
The EMCDDA exists to provide the EU and its Member States with a factual overview of European drug problems and a solid evidence base to support the drugs debate. Today it offers policy makers the data they need for drawing up informed drug laws and strategies. It also helps professionals and practitioners working in the field pinpoint best practice and new areas of research.
Its flag is blue with its logo in the middle of the flag. The logo consists of a blue and yellow rectangle with a white and blue arch, and the 12 stars placed around it. The stars are yellow and blue respectively.
|

EMSA Flag
|
European Maritime Safety Agency
The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) is a European Union agency charged with reducing the risk of maritime accidents, marine pollution from ships and the loss of human lives at sea by helping to enforce the pertinent EU legislation. EMSA was founded in 2002, after the EU adopted substantial packages of legislation relating to maritime security in the wake of major shipping disasters in European waters. It is headquartered in Lisbon.
The EMSA flag is white with the EMSA logo on the flag placing fitted to lower and upper edges, but without the inscription (which is originally part of the official version).
|

ENISA Flag
|
European Network and Information Security Agency
The European Network and Information Security Agency (ENISA) is an agency of the European Union. Its mission is to achieve a high and effective level of Network and Information Security within the European Union. ENISA is helping the European Commission, the Member States and the business community to address, respond and especially to prevent Network and Information Security problems.
ENISA was created in 2004 and is headquartered in Heraklion, Crete (Greece). Its flag is white with a centered blue logo consisting of the 12 stars of the European Union placed in an oval shape with the name ENISA written through the right side of the oval.
|

ESA Flag
|
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA), established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organization dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states. Headquartered in Paris, France, the ESA has a staff of more than 2,000. ESA's space flight program includes human spaceflight, mainly through the participation in the International Space Station program, the launch and operations of unmanned exploration missions to other planets and the Moon, Earth observation, science, telecommunication as well as maintaining a major spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou, French Guiana, and designing launch vehicles.
ESA science missions are based at ESTEC in Noordwijk, Netherlands, Earth Observation missions at ESRIN in Frascati, Italy, ESA Mission Control (ESOC) is in Darmstadt, Germany, the European Astronaut Centre (EAC) that trains astronauts for future missions is situated in Cologne, Germany, and the European Space Astronomy Centre is located in Villanueva de la Cańada, Spain.
|

EUCC Flag

QualityCoast Flag |
Coastal and Marine Union
QualityCoast Award Flag
The Coastal and Marine Union (EUCC) is an association with 2700 members and member organizations in 40 countries. Founded in 1989 with the aim of promoting coastal conservation by bridging the gap between scientists, environmentalists, site managers, planners and policy makers, it has grown since then into the largest network of coastal practitioners and experts in Europe, with 15 National Branches and offices in seven countries. Our working area is Europe, the Mediterranean and Black Sea and other neighboring regions.
The EUCC flag is yellow/gold over blue, the division being an ascending curve starting from the lower fourth of the hoist and reaching the upper right corner. The blue field is charged with the yellow/gold silhouette of a stylized "e" forming a coastal headland, while a vertical yellow/gold lettered "EUC" runs down the blue hoist side. A horizontal blue lettered "Coastal & Marine" crosses the bottom yellow/gold part of the field and completes the design. EUCC Logo and flag are identical.
The QualityCoast Program award goes to coastal communities that integrate their natural, cultural and social values while maintaining high standards in the quality of their tourism. It is an independent certification of the performance of the coastal community and its tourist product which makes use of 20 QualityCoast criteria. It has been developed by the Coastal and Marine Union (EUCC) in a European Union project involving 21 partners from 11 countries. The EUCC is one of the largest coastal expert networks in the world.
The QualityCoast flag has an identical background as the EUCC flag, but the blue field is charged with the yellow silhouette of a jumping dolphin, while "QualityCoast" is written in blue on the yellow field.
|

EUROPOL Flag
|
European Law Enforcement Agency
The European Law Enforcement Agency (EUROPOL) goal is improving the effectiveness and cooperation between the law enforcement agencies in the EU Member States, especially in preventing and combating terrorism, unlawful drug trafficking and other serious forms of organised crime.
Europol has a new logo and new flag. Its flag is dark blue and and orange divided by a narrow white stripe forming a peak of mountain at the fly part of the flag. Its new logo is placed in the upper hoist part of the flag.
|

EUROJUST Flag
|
Eurojust Flag
Eurojust acts like the EU justice system and is a judicial cooperation body created to help provide "safety within an area of freedom, security and justice." Eurojust was set up by the Council of the European Union in 2002 to improve the fight against serious crime by facilitating the optimal co-ordination of action for investigations and prosecutions covering the territory of more than one Member State with full respect for fundamental rights and freedoms.
The EUROJUST flag is white with its logo centered on the field. The yellow EU stars are overlapped by red, yellow, and blue rectangulars, a scale, a sword and inscription are placed on various colors.
|

EUROMIL Flag
|
European Organisation of Military Associations
The European Organisation of Military Associations (EUROMIL) promotes the social and professional interests of military personnel of all ranks in Europe. The Organisaton is the primary Europe-wide forum for co-operation among professional military associations on issues of common concern. EUROMIL is the umbrella organisation of 39 national military associations and trade unions.
Originally founded in 1972, the Organisation includes 25 countries from the Russian Federation in the East to Ireland in the West, and from Finland in the North to Cyprus in the South; EUROMIL is a truly European organisation.. Through the international secretariat in Brussels, EUROMIL facilitates the exchange of information, experiences and best practice among member associations. Its flag is blue with white EU stars, and with its name inside the circle of stars.
|

FINE Flag
|
European Federation of Nurse Educators
(formally "Federation of International Nurse Educators" or simply FINE)
The European Federation of Nurse Educators (FINE) was founded in 1995 in Leuven, Belgium, by a group of nursing teachers from several countries who wished to establish a forum for nurse education in Europe and a place to exchange information and experiences, and acquire better programs of nurse training and education. The association provides a place for the discussion of issues in nursing education and opportunities, and a way to influence important health care policy decisions in Europe. Initially, the countries involved were the Netherlands, Great Britain and Belgium, but soon most members of the European community joined.
The FINE flag is a square variant of the European Union flag that has the bottom five lower gold stars replaced by gold crosses, and the gold initials "FINE" centered within the circle of stars and crosses. Underneath are printed the words "European Federation" and "of Nurse Educators" in gold.
|

FRONTEX Flag
|
European Agency for the Management of Operational Cooperation at the External Borders of the Member States of the European Union
The European Agency for the Management of Operational Cooperation at the External Borders of the Member States of the European Union (FRONTEX) wins the award for the longest agency name in the EU hands down. It is the European Union agency charged for external border security and is responsible for coordinating the activities of the national border guards in ensuring the security of the EU's borders with non-member states. FRONTEX was established in 2004.
FRONTEX is headquartered in Warsaw, Poland. Its flag is white with FRONTEX emblem in the middle of the flag. It consists of 12 EU stars, a green border line and a blue circle. Under this logo the name and its motto are written with blue letters "Liberty, Security, Justice" in Latin.
|

OHIM Flag
|
Office for Harmonization in the Internal Market
The Office for Harmonization in the Internal Market (OHIM) is the trademark and designs registry for the internal market of the European Union. The task of OHIM is to promote and manage Community Trade Marks and Community Designs within the European Union. It carries out registration procedures for titles to EU industrial property and keeps public registers of these titles. It shares with the courts in Member States of the European Union the task of pronouncing judgment on requests for invalidation of registered titles.
The OHIM is based in Alicante, Spain. Its flag white with its logo on it, a blue letter R in the center surrounded by the yellow EU stars in circle.
|

IED Flag
|
Institute of European Democrats
The Institute of European Democrats (IED) was established in September 2007 as a new and independent Research Institute based in Brussels. Its primary goal is to promote a better understanding of the core aspects of the European integration process, and to play an active role in strengthening the confidence of European citizens and their direct participation with regards to European Institutions and policies and, above all, in favour of the idea of a united Europe.
Its flag is white with light blue map of Europe covered with its logo. It contains their abbreviation and name, and five stars (on of them is blue, other four are yellow) in an arc placed above the abbreviation.
|
Flags of the European Union Military Missions
The European Union (EU) is primarily an economic and political union of 27 member states, but they do include military capabilities. In recent years they have been active in several military missions.

EU NAVFOR Flag
|
European Union Naval Force Somalia 2008
The European Union is now conducting a military operation to help deter, prevent and repress acts of piracy and armed robbery off the coast of Somalia. The European Union Forces (EU NAVFOR) are part of an international military organization consisting of forces of European Union countries with their own command structure.
This military operation, named European Union Naval Force Somalia – Operation ATALANTA, was launched in support of Resolutions 1814, 1816, 1838 and 1846 which were adopted in 2008 by the United Nations Security Council. Its mandate is to contribute to the protection of vessels of the World Food Programme (WFP) delivering food aid to displaced persons in Somalia; and the protection of vessels sailing in the Gulf of Aden and off the Somali coast. |

Nordic Battle Group
|
Nordic Battle Group (Sweden, Finland, Norway)
The Nordic Battle Group includes troops from Sweden, Norway, Finland and Estonia. The background to the agreement lies in the European Union's (EU) decision to establish 13 so-called battle groups, each consisting of about 1500 military personnel. The aim is to establish flexible rapid reaction forces capable of deploying at short notice to take part in operations to maintain or re-establish peace and security. The Nordic Battle Group was placed at the disposal of the EU in 2008.
The Nordic Battle Group ensign is a blue square with a heraldic lion holding a sword and an olive branch. The lion is a national symbol of many former and present European kingdoms and the sword and the branch signifies the ambition to impose peace - with or without the use of violence.
|

Commander 5th Battlegroup
|
Commander of the Nordic Battlegroup.
This ensign is that of the Commander of the Nordic Battle Group (Kommandotecknet för Nordic Battlegroup), European Union's 5th battlegroup, which includes military from Sweden, Norway, Finland and Estonia. This Commander´s ensign was first introduced in 2006 in Stockholm, Sweden.
The Nordic Battle Group Commander´s ensign is a square horizontal turban of blue-yellow-blue, with blue Roman numeral V in the yellow stripe. The "V" may also be interpreted as "Victory," referring to the battle group motto: "Victory through Values."
|

Eurocorps Flag
|
EUROCORPS
Eurocorps is a multinational army corps within the framework of the Western European Union common defence initiatives. Eurocorps comprises approximately 1,000 soldiers stationed in Strasbourg and up to 60,000 troops pledged for deployment in EU or NATO rapid-response missions. The nucleus of the force is the Franco-German Brigade established in 1987.
Headquartered in Strasbourg, France, the force was established in 1992 and declared operational in 1995, though it draws from European defence initiatives as far back as the 1960s.
|

Eurofor Flag
|
European Operational Rapid Force
The European Operational Rapid Force (Eurofor) was created in 1995 as a task force of the Western European Union, being operational in June of 1998. It is a multinational rapid reaction force composed of forces from France, Italy, Portugal and Spain. It has a permanent staff capable of commanding operations, involving commitments of up to a light division in size.
The Eurofor flag has an approximate 2:3 rectangular shape, with a blue field on which the Eurofor emblem is centered. The emblem has a red fleur-de-lis on top of a crossed green olive branch and white sword with yellow hilt. It is surrounded on the top by four arched yellow stars, and has a series of three white waves underneath. The size of the Eurofor emblem shown here may not be in correct proportion to the flag size.
|

EMF Flag
|
European Maritime Force
The European Maritime Force (EUROMARFOR or EMF) is an multinational naval force, able to carry out naval, air and amphibious operations and its composition depends on the mission given. EUROMARFOR was born in 1995 when France, Italy, Portugal and Spain agreed to create a tailored force in order to fulfill missions defined in the Petersberg’s Declaration, such as sea control, humanitarian missions, peacekeeping operations, crisis response operations (pre-emptive deployment, maritime patrolling, mine clearing, etc.) and peace enforcement.
The force can be deployed by the EU, as part of the European branch of NATO, or acting upon the mandate of other international organizations, such as UN, WEU, OSCE, or any other multinational coalition. The Euromarfor flag shows four yellow stars and yellow EUROMARFOR written on a blue field.
|

FMP Flag
|
Multinational Protection Force in Albania 1997
In 1997 Albania descended into anarchy and violence in which the government was toppled and some 2,000 people were killed. The United Nations Security Council passed a Resolution authorized a force of 7,000 on March 28 to direct relief efforts and to restore order to Albania. The UN feared the unrest would spread outside Albania's borders and contribute even more refugees to Europe. On April 15, the 7,000 troops launched Operation Sunrise, an Italian-led mission which helped restore rule of law to the country.
The flag of the Multinational Protection Force in Albania (April-August 1997) has a blue field with stars representing the participating countries in the Alba mission. The stars are yellow, which makes the flag resemble the flag of the Council of Europe and the European Union. The stars are arranged in an arch and under the arch are set the letters "FMP" in white. FMP is the acronym for the name of the operation in Italian: Forza Multinazionale di Protezione.
|
|