|
 1st |
 2nd |
 3rd |
 4th |
The following are Unit Indicator Flags
Within NATO, ships may be formed into specific units: Flotilla/Group, Squadron, Division, SubDivision. The four "Unit Indicators" are used to either address or identify specific units when other flags are added to them.
Examples: C Division pt 2 could mean "Cruiser division number 2 (or 2nd cruiser division)." F Squad pt 4 could mean "Frigate squadron number 4 (or 4th frigate squadron)." - Note: "pt" stands for pennant.
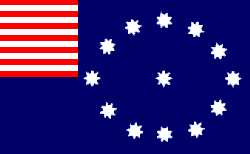
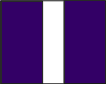
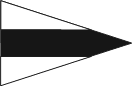
 Flotilla or Group This flag is used to either address or identify specific units when other flags are added to them. A Flotilla/Group may consist of two or more Squadrons |
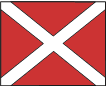
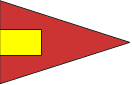
 Squadron This flag is used to either address or identify specific units when other flags are added to them. A Squadron may consist of two or more Divisions. |
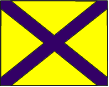
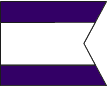
 Division This flag is used to either address or identify specific units when other flags are added to them. A Division may consist of two or more SubDivisions. |
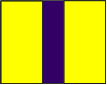
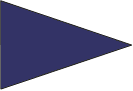 Subdivision This flag is used to either address or identify specific units when other flags are added to them. |
The following are Governing Pennants
Preparative, Interogative and Negative are "governing" pennants. They alter the "sense" of a signal.
Examples: ED 18 (E-D-1-8) means "weigh anchor," but Preparative ED 18 would mean "Prepare to weigh anchor," Interrogative ED 18 would mean "Are you or have you weighed anchor?," and Negative ED 18 means "Do not weigh or stop weighing anchor."
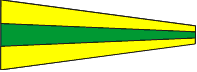 Preparative |
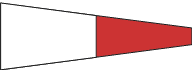 Interrogative |
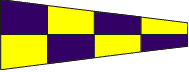 Negative |
The following are Maneuvering Flags
These flags are used to order formations or alter courses and speeds of a group of ships. They are used to indicate that ships or formations should take immediate actions or maneuvers, including emergency actions. Turn, Corpen, Screen, Formation, Station and Speed, with Port and Starboard are maneuvering flags. They can be used to order an action or convey information. Port and Starboard may be used with Turn, Corpen, Formation and Station to indicate direction. The remaining three, Emergency, Desig and Code/Answer can be classified as Special flags.
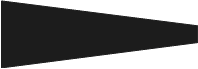 Screen Ships are to form a (protective) screen. i.e. - Screen K - means "Form a sector screen." |
 Formation Ships are to form in specified formation. i.e - Form 1 - means "Ships are to form column in numerical order." |
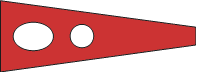 Corpen Course Pennant, used to signal a course or alter the course of a group of ships. |
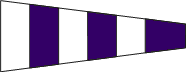 Turn Normally used in conjunction with Port or Starboard for ships to turn together. i.e. - Turn Port 9 - Turn together 90 degrees to port. |
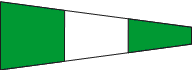 Starboard Used in conjunction with a maneuvering flag to indicate direction. i.e.- Turn Starboard - turn to left |
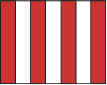 Port Used in conjunction with a maneuvering flag to indicate direction. i.e. - Turn Port -Turn to right |
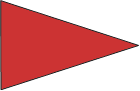 Speed Proceed at a specified speed i.e. - Speed 10 means "The guide of the formation is to proceed at ten knots." |
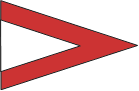 Station Ship(s) indicated are to take a specific station(s) or position. i.e. - Station A - means "Take station ahead." |
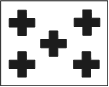
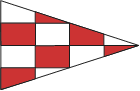 Emergency Action or information that requires immediate attention. i.e. - Emerg C - means "I have been involved in a collision" Emerg 0 - means "All ships scatter." |
Remaining Special Pennants
All the above flags, except the Numeral Flags, are actually classified as Special Flags and Pennants.
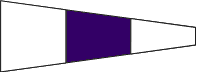 Designation The following is in plain language or is to be read in its literal sense. |
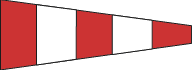 Code or Answering This flag is used to answer or acknowledge a flag signal or indicates that signal following is from the International Code. |
International Code of Signals and Flags
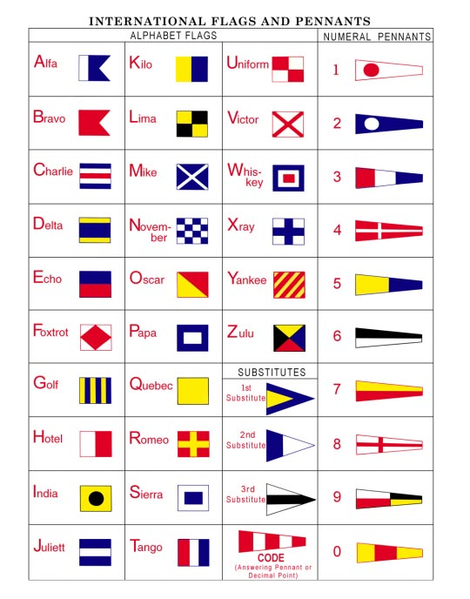 |
North Atlantic Treaty Organization vessels also use the International Code of Signals (ICS) flags and pennants, but not their "numeral" signal flags. The International Code of Signals (ICS) is basically an international system of signals, words, and codes for use by vessels to communicate with each other while at sea. The use of words to vocally clarify letters is an important part of the system. This way signals can be clearly sent by flags, signal lamp (blinkers), semaphores, and electronics. The International Code of Signals was first introduced in 1857 by the British Board of Trade as a means of maritime communications. Originally it had 17,000 signals using 18 flags. Today, it has been modified and adopted by most modern sea-faring nations, and uses symbols from nine major languages: including English, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Spanish, Norwegian, Russian and Greek. |
| Military Missions | Rapid Deployable Corps | Military Centers | Related Non-Military Flags |