Note: If an image ever fails to appear - refresh your page, it really is there
Canadian Provinces and Territories
Canada has 10 provinces, and three northern territories. It is also divided into 11 historic regions. It is the world's second largest country by total area. Canada's common border with the United States to the south and northwest is the longest in the world. The capitol is Ottawa.
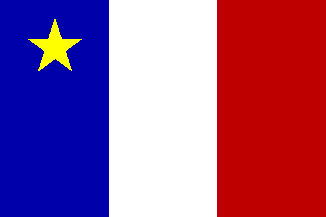
French-Canadian Acadian Flag
1867

Louisiana-Cajun Acadian Flag
1965
|
Historical Region of Acadia Flag 1867
During the British conquest of New France, the British changed the name of the French colony of Acadia to "Nova Scotia" (New Scotland), much to the discuss of the French inhabitants. This rather French looking tricolored flag was introduced in the 1840's as a flag for the French in Canada, at first mostly in the Quebec region, but within 20 years became something of a national flag for all Canadian French-Catholic nationalists.
The yellow star, the Stella Maris, is the symbol of Mary, the Acadian national symbol and patron of the mariners. It is set on the blue stripe, because blue is the color of Mary. The yellow color of the star represents the Papacy.
In the Great Expulsion of 1755-1763, mostly during the Seven Years' War, the British colonial militia deported more than 14,000 Acadians from the maritime region in what can only be called an early case of ethnic cleansing. Approximately one third perished, but many later settled in Louisiana, where they became known as Cajuns.
Since 1965, the Louisiana Acadian flag has been flown throughout Acadiana - the 22-parish area of south Louisiana populated by the Cajun people. Although technically an "American" flag, it is shown here because of its historical "Canadian" connection. (Opening the question of "Are not Canadian's technically Americans also?" - although the thought probably would cause Canadian nightmares...) |

Alberta Flag
|
Province of Alberta Flag
Alberta, one of Canada's three prairie provinces, officially became a province in 1905. It is located in western Canada between British Columbia to the west and Saskatchewan to the east, and the Northwest Territories to the north, and borders the United States (Montana) to the south. It is one of two Canadian provinces that is completely landlocked (the other being Saskatchewan).
In 1958, the Alberta adopted its official flag with the provincial shield of arms in the center of a royal ultramarine blue background. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Alberta
The official website of the Lieutenant Governor describes the flag as
follows: "The Lieutenant Governor's flag is flown over the Legislature Building when the Lieutenant Governor is present. As well, it is flown at the Lieutenant Governor's official residence when the Lieutenant Governor is there, and it is mounted on the Lieutenant Governor's automobile when it is being used for official business."
|

British Columbia Flag
|
Province of British Columbia Flag
British Columbia, the westernmost of Canada's provinces, became the sixth province of Canada in 1871. Known for its natural beauty, its name was chosen by Queen Victoria herself in 1858. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, the fifteenth largest city in Canada, and located on Vancouver Island.
At the top of the flag is a rendition of the Union Flag, defaced in the center by a crown, representing the province's origins as a British colony. The three wavy blue lines symbolize the province's location between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, and the setting sun represents the fact that British Columbia is Canada's westernmost province. Some early versions of the flag were reversed, with the Union Flag on the bottom. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of British Columbia
The official website of the Lieutenant Governor describes the flag as
follows: "The Lieutenant Governor's Flag is a royal blue flag with the shield of arms of British Columbia in its centre, surrounded by a circlet of 10 gold stylized maple leaves representing the 10 Provinces of Canada. Above the shield is a St. Edward's Crown, signifying the Sovereign´s representative in the Province."
"The flag was approved by the Governor General on behalf of Her Majesty The Queen on February 1, 1982. When the Lieutenant Governor is present, the flag is flown at public buildings, Canadian Forces' establishments, the Parliament Buildings, on Her Majesty's Canadian Ships and at Government House."
|

Manitoba Flag
|
Province of Manitoba Flag
Manitoba is another of Canada's flat prairie provinces whose major industries are agriculture, mining, forestry, and tourism due to natural beauties. Although its main population is English Canadian, there is a significant Franco-Canadian minority with a growing Native-American population. Manitoba is one of the most important centers of Ukrainian culture outside Ukraine and home to the largest Icelandic community outside of Iceland. Manitoba's capital and largest city is Winnipeg, Canada's eighth-largest city.
The Flag of Manitoba is a standard Red Ensign which bears the shield of the provincial coat of arms. This flag was chosen and then approved by Queen Elizabeth II in 1965, and first flown in 1966. The decision to adopt the flag was made after the federal government decided to replace the Canadian Red Ensign with the Maple Leaf flag. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Manitoba
As stated on the official website, "The Lieutenant Governor of Manitoba is the viceregal representative in Manitoba of the Canadian monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, who operates distinctly within the province, but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada and resides predominantly in her oldest realm, the United Kingdom."
The Lieutenant Governor of Manitoba is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties.
|
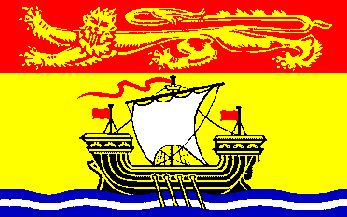
New Brunswick Flag
|
Province of New Brunswick Flag
New Brunswick, one of Canada's oldest three Maritime provinces, is the only official constitutionally bilingual province (English and French) in the federation. The capital is Fredericton, but Saint John is the most populous city. The majority of the population is English-speaking, but there is also a large French-speaking minority (33%) mainly of Acadian origin. The province's name comes from the English and French partial transcription of the city of Braunschweig in northern Germany, the ancestral home of the Hanoverian King George III of Great Britain.
The flag of New Brunswick is a banner modelled after the province's coat-of-arms and was adopted in 1965. The gold lion on the red field stretching across the top one-third of the flag represents New Brunswick's ties to the Brunswick region in Germany and the arms of the Monarch of the United Kingdom. The lower two-thirds of the flag depicts a Spanish galley representing shipbuilding, one of the province's main industries at the time the coat of arms was adopted. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of New Brunswick
The official website of the Lieutenant Governor describes the flag as follows: "a royal blue flag, two by width and three by length, the shield of the Arms of the Province surrounded by a circlet of ten gold stylized maple leaves, representing the ten Provinces of Canada. Above all a St. Edward's Crown in proper colours, representing the Sovereign's representative in the Province."
"This flag is flown at Government House, and from the Legislative Buildings whenever the Lieutenant-Governor is in Fredericton. It is also flown from public buildings throughout the province whenever the Lieutenant-Governor happens to be in residence."
|
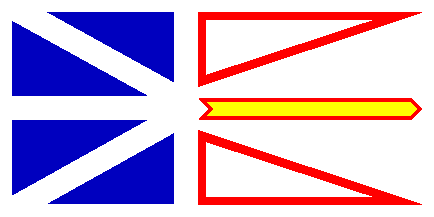
Newfoundland and Labrador Flag
|
Province of Newfoundland and Labrador Flag
Newfoundland and Labrador is located on the Atlantic coast of Canada consisting of the island of Newfoundland and Labrador on the mainland. It became the tenth province in 1949, at first simply named Newfoundland. In 2001, the province's official name was changed to Newfoundland and Labrador, although most Canadians generally still refer to the province as Newfoundland and to the region on the Canadian mainland as Labrador.
The "Golden Shaft" flag of Newfoundland and Labrador was designed by the Newfoundland artist Christopher Pratt in 1980. The blue color represents the sea, the white color represents the snow and ice of winter, the red color represents the effort and struggle of Newfoundlanders and Labradorians, and the gold color symbolizes their confidence in themselves and the future. The blue triangles represent the Union Flag and their British heritage. The two red triangles represent the two areas of the province. The gold arrow points towards a "brighter future" with the arrow becoming a sword, honouring the sacrifices of Newfoundlanders in military service when the flag is draped as a vertical banner. The red triangles and the gold arrow form a trident, symbolizing the province's dependence on its fisheries and the resources of the sea. Learn more about the Flags over Newfoundland and Labrador. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Newfoundland and Labrador
The Lieutenant Governor of Newfoundland and Labrador is the viceregal representative in Newfoundland and Labrador of the Canadian monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, who operates distinctly within the province, but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada and resides predominantly in her oldest realm, the United Kingdom.
The Lieutenant Governor of Newfoundland and Labrador is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties. |

Northwest Territories Flag
|
Northwest Territories Flag
The Northwest Territories is located in northern Canada. It borders two other territories, Yukon to the west and Nunavut to the east, and the three provinces of British Columbia, Alberta and Saskatchewan. Since 1967 Yellowknife has been the territorial capital.
The original flag of the territory was the Hudson's Bay Company until 1950. It was replaced by a standard royal blue ensign with the territorial coat-of-arms placed in a white circle on the fly that was used between the years 1950-1969. The current flag, without the union jack in the canton, is the result of a flag design contest and reuses the coat-of-arms from the old flag, but places it on the wider center stripe of new tricolor blue-white-blue design. The blue represents the Northwest Territories waters, and the white represents snow and ice. |

Territorial Commissioner´s Flag
|
Flag of the Commissioner of the Northwest Territories
According to the official website, "The Commissioner of the Northwest Territories serves a pivotal role in the governance of the Northwest Territories. Appointed by the Governor-in-Council of Canada on the recommendation of the Minister of Indian Affairs and Northern Development, the Commissioner is the federal government's representative in the north and the Chief Executive Officer of the Northwest Territories."
"Unlike the provinces, the Northwest Territories is not given the authority to govern under the Constitution Acts. The position of Commissioner is created by the federal Northwest Territories Act and exercises a function similar to that of a provincial Lieutenant Governor." |

Nova Scotia Flag
|
Province of Nova Scotia Flag
Nova Scotia (New Scotland) is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The provincial capital is Halifax. In 1604, French colonists established the first permanent European settlement in Canada and the first north of Florida at Port Royal, founding what would become known as Acadia. The British Conquest of Acadia happened in 1710. At this time the Capital Port Royal was renamed Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia. The capital of Nova Scotia moved from Annapolis Royal to the newly established Halifax in 1749. In 1867, Nova Scotia was one of the four founding provinces of the Canadian Confederation.
The current Flag of Nova Scotia, created in 1858, is based on the coat-of-arms granted to the Scottish colony by Charles I, King of Scots. The flag, a blue saltire on a white field, is a simple color reversal of the flag of Scotland, bearing the royal arms of Scotland, a gold shield with a red lion. The royal arms were added to the Nova Scotia flag to distinguish the flag from the Naval Ensign of Russia which is also a blue saltire on a white field. Nova Scotia was one of the few Canadian colonies to be granted its own coat-of-arms, and the flag is the only one of the Canadian provinces dating back to before confederation. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia
The Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia is the viceregal representative in Nova Scotia of the Canadian monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, who operates distinctly within the province, but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada and resides predominantly in her oldest realm, the United Kingdom. The Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties.
Until 1786 the vice-regal representative in Nova Scotia normally held the rank of Governor, and only occasionally Lieutenant Governor. Since then, all have been Lieutenant Governors. During periods where no vice-regal representative was in office, an Administrator was in charge.
|

Nunavut Flag
|
Nunavut Territory Flag
In 1992, a referendum was passed authorizing the separation of the eastern half of the Northwest Territories to create a new autonomous territory, to be called Nunavut (pronounced noo-na-voot), which is Inuktitut for "Our Land."
Nunavut officially came into existance as a Canadian territory on April 1, 1999. It is both the least populous and the largest geographical unit of all the provinces and territories of Canada. Nunavut's Chief Executive is a Commissioner appointed by the Federal Minister of Indian Affairs and Northern Development. |

Territorial Commissioner´s Flag
|
Flag of the Commissioner of the Nunavut Territory
As in the other territories, the Commissioner's role is symbolic and is analogous to that of a Lieutenant-Governor. While the Commissioners are not formally a representative of Canada's head-of-state, they have a role representing The Crown in a territory.
|
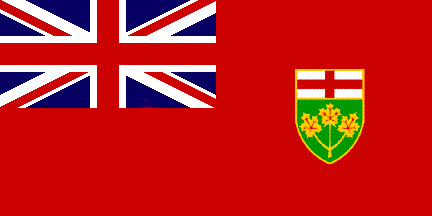
Ontario Flag
|
Province of Ontario Flag
Ontario is the second largest Province of Canada located in the east-central part of Canada. The province is named after Lake Ontario, which is thought to have been derived from a Huron word meaning "great lake." The province's largest city is Toronto, is the capital city of Ontario, and the national capital of Canada, Ottawa, is also located in Ontario. Ontario is bordered by Manitoba, Hudson Bay, Quebec, and by three states of the United States (Minnesota, Michigan, and New York), and Lake Erie.
The Flag of Ontario was first used in 1965. The flag is a defaced Red Ensign, with the Union Flag in the canton and the Ontario coat-of-arms in the fly. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Ontario
The official website of the Lieutenant Governor describes the flag as
follows: "The Standard is a royal blue flag featuring the shield of the Arms of Ontario encircled by ten gold maple leaves to represent Canada's provinces and surmounted by a Crown to symbolize the role of the Lieutenant Governor as The Queen's representative. The Standard is flown outside the Lieutenant Governor's Suite at Queen's Park when His Honour is in the provincial capital. It is displayed in his office and in the Music Room, where ceremonies take place. It is mounted on the car in which His Honour travels and is flown outside of buildings where he is on an official visit."
"In Ontario, the Lieutenant Governor's standard takes precedence over all other flags, except for the standard of The Queen and, on some occasions, that of the Governor General. Created at the request of the Ontario government, this standard was approved by the Governor General in 1981, as the first in a series of vice-regal standards now introduced in all provinces."
|

Former Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Ontario 1959-1965
This was the Standard of the Lieutenant Governor of Ontario from 1959 to 1965. The office of Lieutenant Governor of Ontario was established in 1867, replacing the position of Lieutenant Governor of Canada West. The office became a target for Government cutbacks in 1837 by the Liberal Party and Ontario Government House was closed until 1985 with the Viceroy working out of a suite at the Legislative Building.
In 1959, this unusual red ensign was put in use by Lieutenant Governor J. Keiller Mackay to show his support for the campaign to make the Canadian Red Ensign of 1957-1965 the national flag of Canada. This was the only Canadian Lieutenant Governor's flag of this pattern. This new Lieutenant Governor's flag, introduced in April of 1959, was used at Queen's Park and on his car. After 1965, the previous defaced Union Jack, similar to that used today by the Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia, was restored. In 1981, the present Lieutenant Governor's Flag was adopted and replace the earlier versions. |

Prince Edward Island Flag
|
Province of Prince Edward Island Flag
In 1873, Prince Edward Island became the seventh Canadian province consisting of Prince Edward Island and several other smaller islands. This maritime province is the smallest in the nation.
The island was named for Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (1767–1820), the fourth son of King George III and the father of Queen Victoria.
The flag of Prince Edward Island is modelled after the provincial arms. It is bordered by alternating bands of red and white, with the upper third of the flag the English lion which appeared both on the coat-of-arms of Prince Edward, and on that of King Edward VII. The lower two-thirds show an island on which appear three small oak saplings representing the three counties of Prince Edward Island under the protection of a great oak tree which represents Great Britain. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Prince Edward Island
The post of Lieutenant Governor was established in 1769 as part of the initial administration of the Island colony. The British North America Act of 1867 created Canada and a national (or federal) government, and local (or provincial) governments in the former British North American colonies. The Lieutenant Governor, who had formerly reported to the Colonial Office in London, became initially, an officer of the Government of Canada. In Prince Edward Island, this change took place in 1873 when the colony exchanged its earlier status for that of a province of the Dominion of Canada.
Since the Statute of Westminister of 1931, Canada has been a fully sovereign country; however, Canada has chosen to remain a member of the Commonwealth, a voluntary association of independent states representing approximately 25 percent of the world's population. Her Majesty, Queen Elizabeth of the United Kingdom, is Canadian Head of State and thus, The Queen of Canada. |

Quebec Flag
|
Province of Quebec Flag
Quebec is a province in east-central Canada. Most of its inhabitants live in urban areas near the Saint Lawrence River between Montreal and Quebec City, the capital. It is the only Canadian province predominantly French-speaking and the only one whose sole official language is French.
The flag of Quebec, called the Fleurdelisé, was adopted for the province by the government of Quebec during the administration of Maurice Duplessis. It was the first provincial flag officially adopted in Canada in 1948. |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Quebec
The Lieutenant Governor of Quebec is the viceregal representative in Quebec of the Canadian monarch, Queen Elizabeth II, who operates distinctly within the province, but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada and resides predominantly in her oldest realm, the United Kingdom.
The Lieutenant Governor of Quebec is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties. By virtue of a Royal Commission, the Lieutenant Governor has all of the constitutional powers of a head of state and gives force of law to the policies determined by the government. |

AFC Flag
|
Franco-Ontariens Flag
The first French speakers to come to Ontario were the missionaries who established the mission of Sainte-Marie-among-the-Hurons in 1639. Today there are about 535,000 Francophone people in Ontario, and a flag for this community was adopted by the Association Canadienne-Francaise de l'Ontario (AFC). Her Majesty, the Queen of England, "by and with the advice and consent of the Legislative Assembly of the Province of Ontario", in 1989 recognized this flag as that of the Ontario French-speaking community.
The emblem of the Ontario French-speaking community consists of two vertical bands of different colors. The first band is mid-green and has a white lily in the middle of the band. The second band is white and has a green trillium in the middle of the band. On the emblem, green represents summer and white represents winter. Together the two colors represent the diversity of Ontario's climate. The lily evokes the French-speaking community worldwide, whereas the trilliumis the floral emblem of Ontario. |

Saskatchewan Flag
|
Province of Saskatchewan Flag
Saskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which is bounded on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the American states of Montana and North Dakota. The provincial capital is Regina, but the largest city is Saskatoon. Saskatchewan was first explored in 1690 and settled in 1774, but prior to that, it was populated by several native tribes. It became a province in 1905.
The flag of Saskatchewan features the coat-of-arms in the upper quarter with the floral emblem, the western red lily, in the fly. The upper green half of the flag represents the northern Saskatchewan forest lands, while the gold lower half symbolizes the southern, prairie wheat-fields |

Lt. Governor´s Flag
|
Flag of the Lieutenant Governor of Saskatchewan
Canada's Constitution recognizes The Queen as the Head of State. The Lieutenant Governor represents The Queen in the Province of Saskatchewan. The Lieutenant Governor plays an important role as the representative of the Head of State, reading the Speech from the Throne, formally appointing Premiers and Cabinet Ministers, opening and proroguing (closing) Legislative Sessions, approving legislation, and bestowing honours.
In addition to constitutional duties, the Lieutenant Governor is involved with many organizations in the role of honorary patron. The Lieutenant Governor attends hundreds of events each year and receives diplomatic visitors.
|
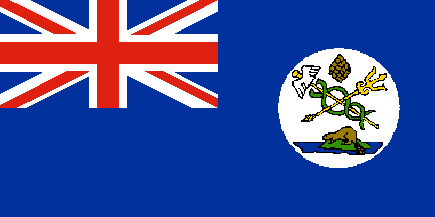
Vancouver Island Flag
|
Historical Region of Vancouver Island Flag
The historic Island of Vancouver is located in British Columbia. It is named after British Royal Navy Captain George Vancouver, who between 1791 and 1794 explored the Pacific Northwest coast of North America. Captain James Cook spent a month during 1778 on Vancouver Island and claimed it for England.
In 1789, Esteban José Martínez explored Vancouver Island for Spain. The Spanish established a settlement and a fort at this time. This was the only Spanish settlement ever established in Canada. To counter this Spanish interest in the area, Captain Vancouver was sent to the Pacific Northwest to negotiate with the Spanish.
Shortly thereafter, in 1846, the Oregon Treaty was signed by the British and the U.S. to settle the question of the U.S. Oregon Territory borders. It awarded all of Vancouver Island to the British, despite a portion of the island lying south of the 49th parallel. In 1849, the Colony of Vancouver Island was established. |

Yukon Territory Flag
|
Yukon Territory Flag
The Yukon Territory is the westernmost and smallest of Canada's three federal territories. It was named after the Yukon River. The territory's capital is Whitehorse. The territory was created in 1898. The largest ethnic group in the territory is English, followed by First Nations. Yukon law recognizes First Nations languages, but only considers French and English as official languages.
The flag of Yukon is a green, white, and blue tricolor with the coat-of-arms of Yukon at the center above a wreath of fireweed, the territorial flower. The Flag of Yukon was officially selected from a territory-wide design competition in 1967, with the winning design adopted in 1968. |

Territorial Commissioner´s Flag
|
Flag of the Commissioner of the Yukon Territory
The Commissioner is appointed by the Government of Canada. Her role is very similar to a provincial lieutenant governor. The Commissioner is Yukon's head of state and generally acts on the advice of elected officials.
One of the Commissioner's most important responsibilities is to ensure Yukon has a Premier at all times. If the Office of the Premier becomes vacant due to a resignation or death, it is the duty of the Commissioner to ensure the post is filled. If the government resigns following a defeat in the legislature or in an election, the Commissioner has the same responsibilities. |
| Top of This Page | The National Flags of Canada |
|